- Facts
- Shoroq Samir
Ancient Egypt and The Egyptian Civilization
It was never just a kingdom or just a country, it was the beginning of humanity and the place where the first men started to rise and build one of the oldest civilizations on earth, even some said that the Egyptian civilization was the first of its kind on the earth planet. The existence of the Nile River has helped for sure to create the ancient Egypt kingdom and the Egyptian civilization. Before the official ruling dynasty descend the throne and establish the old kingdom, Egypt was inhabited by the first Egyptians men or norms.

Ancient Egypt
Before upper and lower Egypt get united by king Mena or known as King Narmer, each part was divided into administrative departments have its own governmental regime, traditions and languages. Thousands of years before the advent of the pharaonic Egypt, a group of people gathered inland and practiced agriculture for starters both in the delta and the Nile valley, slowly but surely the culture began to rise over time, and it gradually began to develop among these early inhabitants was to become the infrastructure upon which the phenomenal Egyptian culture was built. Some theories came out trying to prove and explain how the Egyptian culture was manipulated by a group of a new master race, eventually were proven false, it is true that some cultural influence from basic agriculture and water resources.
The Egyptian dynasties
The first dynasty of the Egyptian royal house was first established when king Narmer united Upper and Lower Egypt and took Memphis as the capital of the kingdom. The first dynasty built some stepped pyramids and royal tombs in Memphis and Horus was the state god and the principal deity of the monarchs. Then, the old kingdom started and was founded by the 3rd and 6th dynasties who were recognized for their stepped (Mastaba) tombs and the most popular is king Djoser stepped pyramids at Sakkara. Between the old kingdom and the middle kingdom, there is an intermediate period that includes the 7th and 10th dynasties.
The middle kingdom consists of 11th and 13th dynasties who were popular with Theban art and Amun as the principal god of Thebes. The best example of the new Theban art is the king Mentuhotep funerary monument at Dier Al Bahari. The second intermediate period held by the 14th to 17th dynasties, this period when the Hyksos occupied the delta and middle Egypt, but the king Ahmose from the 18th dynasty put an end to the Hyksos and their culture and the new kingdom started with the 18th dynasty followed by the Ramesside new kingdom period represented by the 19th and 20th dynasties. Between two main periods comes an intermediate period, the third intermediate period comes right before the late period represented by the 26th or 30th dynasties.
Hieroglyphic language
the massage that the text wants to deliver.
The hieroglyphic texts are so hard to be read but once you learn the sequences of symbols and signs, you will be able to understand the delivered message, especially that the hieroglyphic language depends on pictures and clear symbols to symbolize the information behind any text. the language was spoken from 32000 B.C until the middle ages and was considered as holy scripts by the Egyptians. it has more than a thousand different signs and sounds are usually written in rows or in columns upside down.
Literature and art
Egyptians were known for writing scripts and literature on the pyramids and coffins, ancient Egyptians wrote poetry and tales, they also wrote an autobiography on the royal tombs. Narrative literature examples were found such as "story of sinuhe" which is considered one of the ancient Egyptian literature's first works. The story narrates the afterlife journey for king Amenhotep the first, the founder of the 12th dynasty. Middle Egypt was the thriving language of Egyptian literature. The west car papyrus was also written in the same language by one of the anonymous authors, yet the piece is considered one of the Egyptian classics. It is a set of five stories about miracles performed by some magicians in the royal court of king Khufu of the 4th dynasty, each story was told by one of king Khufu sons. The west car papyrus is now displayed in the Egyptian Museum in Berlin.
A one can simply tell that Ancient Egyptians were extremely artistic from the paintings and carvings on their temples and tombs, some of the paintings still maintain their colours. Decorating images and colourful texts were all over coffins, walls and statues with the really authentic artistic style of simple lines, bright colours and shapes of lily and lotus flowers that reflect the Egyptian identity. Ancients Egyptians used many materials for their artistic works such as stone and wood as a cheaper substitute, as well as colours, were obtained from mineral materials such as some plants mixed with Arabic gum or water. Pharaohs used reliefs to commemorate their victories and battles, and king Narmer palette is a fine
example and proof, it is also an example of carving art that the Egyptians were skillful at.
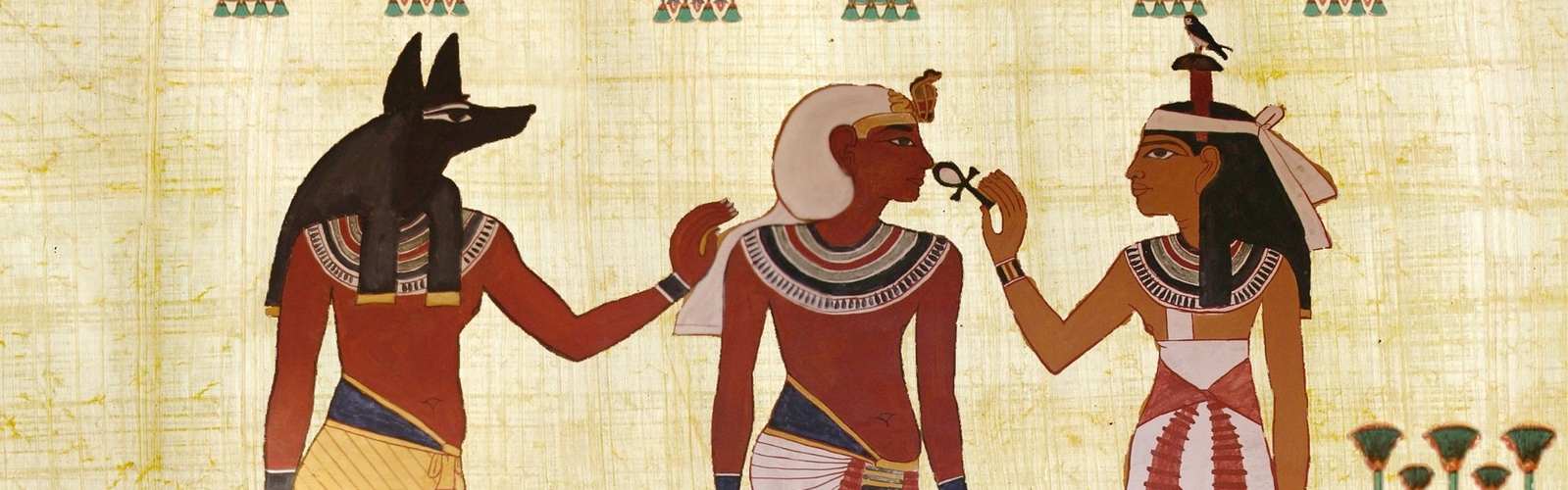
Egyptian gods and religion
Ancient Egypt had enough gods suit everyone's tastes. From fertility gods and sun gods to war and death gods, there was always a blank space to add more gods whether from other foreign cultures or by combining some Egyptian deities. There were main feature gods principal of the state such as Horus, Amon, Osiris, Isis, path and thoth, but the small communities and private temples had their own regional private gods such as Bastet, Nekhbet and Khunso. Each god had his own image and was representing main theme or some religious morals. For example, the god Horus usually painted on the temples as the falcon-headed god with a double crown representing divine kingship. Osiris was a god of the underworld, also known as a god of fertility and her function was judging the dead, usually depicted as a green-skinned man dressed as royal pharaoh. There were also female goddesses such as Hathor, goddess of the sky, sun, love and art. She usually was depicted on the temples as a cow holding the sun between is horns and sometimes painted as a beautiful queen with cow horns. Functions and tasks were divided between deities according to gender. For example, the task of guarding necropolises was given to a male deity, goddess Hathor was also, the guardian of the necropolis and the Egyptians dedicated her a temple named (Hathor temple) in Dendera located west of Luxor city